Fronts and air masses worksheet answer key: Embark on a journey to decipher the intricate dance of atmospheric phenomena that shape our weather. This comprehensive guide unlocks the secrets of fronts and air masses, empowering you with the knowledge to unravel the complexities of weather patterns.
Delve into the dynamic interactions between air masses of varying temperatures and moisture, and witness how they orchestrate the symphony of weather conditions we experience. Understand the distinct characteristics of cold fronts, warm fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts, and unravel the mysteries of their associated weather patterns.
1. Definition of Fronts and Air Masses
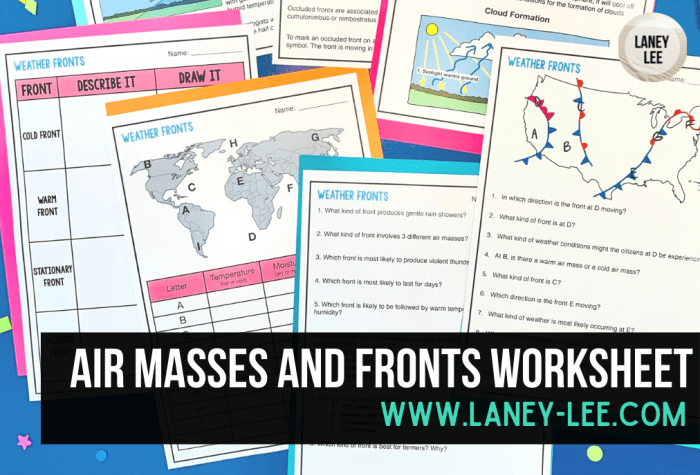
Fronts are boundaries between two air masses with different temperatures and densities. Air masses are large bodies of air that have similar temperature, humidity, and stability characteristics. There are four main types of fronts:
- Cold frontsoccur when a cold air mass pushes a warm air mass upward. They are characterized by steep slopes, narrow bands of precipitation, and rapid changes in temperature.
- Warm frontsoccur when a warm air mass pushes a cold air mass upward. They are characterized by gentle slopes, wide bands of precipitation, and gradual changes in temperature.
- Stationary frontsoccur when a cold air mass and a warm air mass meet and neither is able to move the other. They are characterized by persistent cloud cover and precipitation.
- Occluded frontsoccur when a cold front overtakes a warm front. They are characterized by a complex structure and often produce heavy precipitation.
2. Weather Associated with Fronts
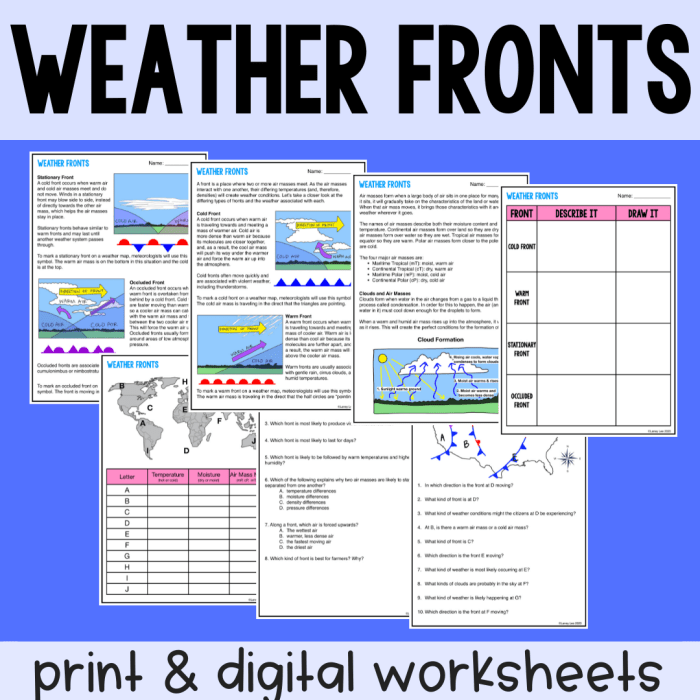
Fronts can cause a variety of weather conditions, depending on the type of front and the characteristics of the air masses involved. Cold fronts typically bring cool, dry air and can cause thunderstorms, squalls, and hail. Warm fronts typically bring warm, moist air and can cause drizzle, rain, and fog.
Stationary fronts can cause prolonged periods of cloud cover and precipitation. Occluded fronts can produce heavy precipitation, thunderstorms, and even tornadoes.
Fronts can also affect local weather patterns. For example, a cold front can bring a sudden drop in temperature, while a warm front can bring a period of mild weather. Fronts can also cause changes in wind direction and humidity.
3. Air Mass Properties
Air masses are characterized by their temperature, humidity, and stability. The temperature of an air mass is determined by the latitude at which it originates. The humidity of an air mass is determined by the amount of water vapor it contains.
The stability of an air mass is determined by the difference in temperature between the air near the ground and the air at higher altitudes.
There are four main types of air masses:
- Continental polar (cP)air masses are cold and dry, and originate over high-latitude land areas.
- Maritime polar (mP)air masses are cool and moist, and originate over high-latitude oceans.
- Continental tropical (cT)air masses are warm and dry, and originate over low-latitude land areas.
- Maritime tropical (mT)air masses are warm and moist, and originate over low-latitude oceans.
4. Air Mass Interactions: Fronts And Air Masses Worksheet Answer Key

Air masses interact with each other when they come into contact. The interaction between two air masses can lead to the formation of fronts. For example, when a cold air mass meets a warm air mass, a cold front can form.
When a warm air mass meets a cold air mass, a warm front can form.
Air mass interactions can also lead to the modification of air masses. For example, when a cold air mass moves over a warm ocean, it can become warmer and more humid. When a warm air mass moves over a cold land area, it can become cooler and drier.
5. Worksheet Analysis
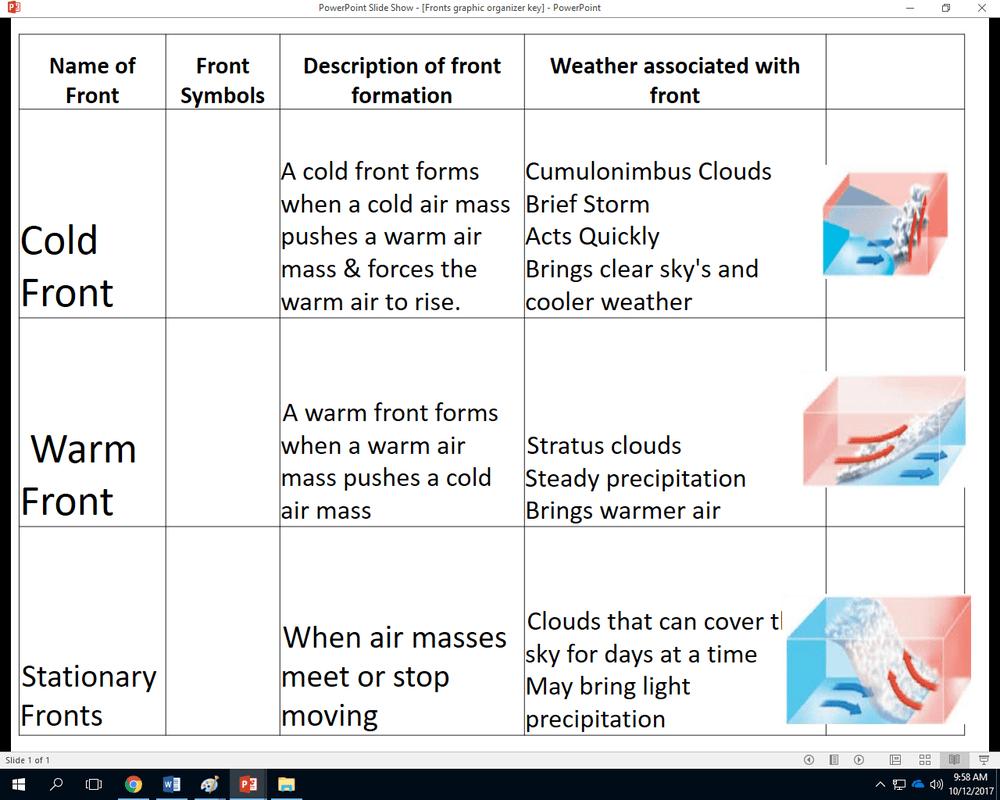
A “Fronts and Air Masses Worksheet” typically contains a map of weather fronts and air masses. The worksheet may also include questions about the weather conditions associated with the fronts and air masses. To analyze a “Fronts and Air Masses Worksheet”, you should first identify the fronts and air masses on the map.
Then, you should answer the questions about the weather conditions associated with the fronts and air masses.
The following steps can help you analyze a “Fronts and Air Masses Worksheet”:
- Identify the fronts and air masses on the map.
- Determine the type of each front (cold, warm, stationary, or occluded).
- Identify the source region of each air mass.
- Predict the weather conditions associated with each front and air mass.
- Answer the questions on the worksheet.
General Inquiries
What is the difference between a cold front and a warm front?
Cold fronts are characterized by the rapid advance of cold air, displacing warmer air, while warm fronts involve the gradual replacement of cold air by warmer air.
How do air masses influence local weather patterns?
Air masses carry distinct temperature and moisture characteristics, influencing local weather conditions such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
What is the role of fronts in the formation of precipitation?
Fronts create zones of convergence where air masses of different temperatures and moisture content meet, leading to the formation of clouds and precipitation.