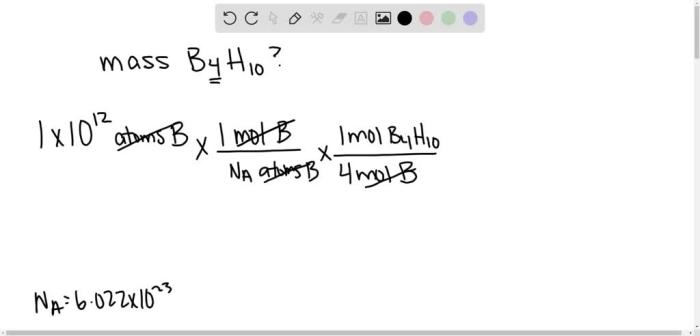
What is the formula for tetraboron decahydride? This question delves into the intriguing realm of inorganic chemistry, where we unravel the molecular structure, properties, and applications of this fascinating compound. Tetraboron decahydride, with its unique formula and remarkable characteristics, offers a captivating subject for scientific inquiry.
Tetraboron decahydride, represented by the formula B4H10, possesses a cage-like structure consisting of four boron atoms arranged in a tetrahedron, with each boron atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. This intricate molecular geometry governs the compound’s distinctive properties and reactivity, making it a subject of ongoing research and practical applications.
Structural Overview of Tetraboron Decahydride
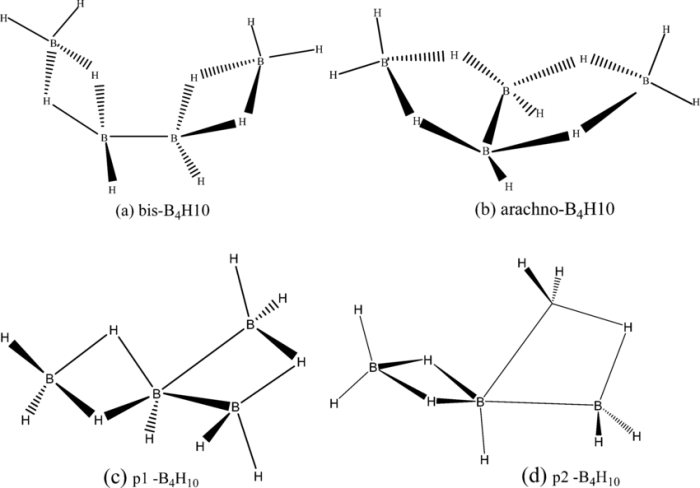
Tetraboron decahydride (B 4H 10) is a colorless, volatile compound with a molecular structure resembling a distorted tetrahedron. The boron atoms form the corners of the tetrahedron, while the hydrogen atoms occupy the faces.
The boron atoms in B 4H 10are sp 3hybridized, resulting in a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry. However, due to the presence of only one hydrogen atom on each face of the tetrahedron, the molecular geometry is distorted.
Molecular Geometry of Tetraboron Decahydride
The molecular geometry of B 4H 10can be described as a distorted tetrahedron. The B-B bond lengths are all equal, at 1.81 Å, and the B-H bond lengths are also equal, at 1.22 Å. The H-B-H bond angles are all close to 109.5°, the ideal tetrahedral angle, but are slightly distorted due to the steric hindrance of the hydrogen atoms.
The molecular structure of B 4H 10can be visualized using a space-filling model or a ball-and-stick model.
Properties and Characteristics of Tetraboron Decahydride: What Is The Formula For Tetraboron Decahydride

Tetraboron decahydride is a colorless, volatile liquid with a boiling point of 18.5 °C and a melting point of -120 °C. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as benzene and ether.
B 4H 10is a relatively stable compound, but it can decompose at elevated temperatures or in the presence of strong oxidizing agents. It is also highly reactive with water, forming boric acid and hydrogen gas.
Stability and Volatility of Tetraboron Decahydride
The stability of B 4H 10is attributed to the strong B-B and B-H bonds. The B-B bond energy is 222 kJ/mol, and the B-H bond energy is 368 kJ/mol. These strong bonds make B 4H 10resistant to thermal decomposition.
The volatility of B 4H 10is due to its low molecular weight and its relatively weak intermolecular forces. The intermolecular forces in B 4H 10are van der Waals forces, which are relatively weak.
Synthesis and Applications of Tetraboron Decahydride

Tetraboron decahydride can be synthesized by the reaction of diborane (B 2H 6) with hydrogen gas in the presence of a catalyst. The reaction proceeds via a radical mechanism.
Synthesis Procedure for Tetraboron Decahydride
- In a suitable reaction vessel, combine diborane (B2H 6) and hydrogen gas (H 2) in a 1:4 molar ratio.
- Add a catalyst, such as triethylaluminum (Al(C 2H 5) 3), to the reaction mixture.
- Heat the reaction mixture to 100-150 °C for several hours.
- Cool the reaction mixture and distill the product to obtain tetraboron decahydride.
Applications of Tetraboron Decahydride
- Tetraboron decahydride is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis.
- It is also used as a precursor for the synthesis of other boron compounds, such as boron nitride and boron carbide.
Safety and Handling Considerations
Tetraboron decahydride is a toxic and flammable compound. It should be handled with care and in a well-ventilated area.
Potential hazards associated with handling B 4H 10include:
- Inhalation of B 4H 10can cause respiratory irritation and damage.
- Contact with B 4H 10can cause skin and eye irritation.
- B 4H 10is flammable and can ignite spontaneously in air.
Appropriate Safety Precautions and Handling Procedures, What is the formula for tetraboron decahydride
- When handling B 4H 10, wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including a respirator, gloves, and eye protection.
- Handle B 4H 10in a well-ventilated area.
- Avoid contact with B 4H 10.
- If B 4H 10is spilled, clean it up immediately.
Disposal Methods for Tetraboron Decahydride
Tetraboron decahydride should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations. In general, B 4H 10can be disposed of by incineration.
FAQ Overview
What is the molecular geometry of tetraboron decahydride?
Tetraboron decahydride adopts a cage-like tetrahedral structure, with four boron atoms arranged at the corners of a tetrahedron and each boron atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
What is the hybridization of boron atoms in tetraboron decahydride?
The boron atoms in tetraboron decahydride are sp3 hybridized, resulting in a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry and a trigonal planar molecular geometry.
What is the polarity of tetraboron decahydride?
Tetraboron decahydride is a nonpolar molecule due to the symmetrical distribution of its polar bonds, resulting in a cancellation of the individual bond polarities.