Welcome to the captivating realm of endothermic and exothermic reactions! In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate world of these reactions, exploring their fundamental concepts, contrasting their characteristics, and unraveling their diverse applications. With our meticulously crafted endothermic vs exothermic worksheet answers, you’ll gain a profound understanding of these intriguing chemical processes.
Throughout this journey, we’ll shed light on the energy transformations that define endothermic and exothermic reactions, unraveling the mysteries behind their distinct behaviors. We’ll delve into real-life examples, demonstrating how these reactions shape our world in countless ways.
Endothermic Reactions
Endothermic reactions are chemical reactions that absorb energy from their surroundings in order to proceed. This means that the products of the reaction have a higher energy content than the reactants.
Examples of endothermic reactions include:
- The melting of ice
- The boiling of water
- The decomposition of calcium carbonate
In endothermic reactions, the energy change is positive, indicating that energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
Exothermic Reactions
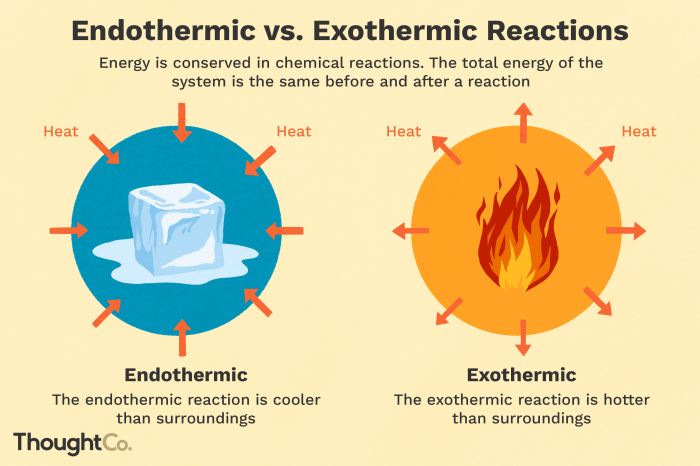
Exothermic reactions are chemical reactions that release energy into their surroundings as they proceed. This means that the products of the reaction have a lower energy content than the reactants.
Examples of exothermic reactions include:
- The burning of wood
- The rusting of iron
- The neutralization of an acid and a base
In exothermic reactions, the energy change is negative, indicating that energy is released into the surroundings.
Comparing Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
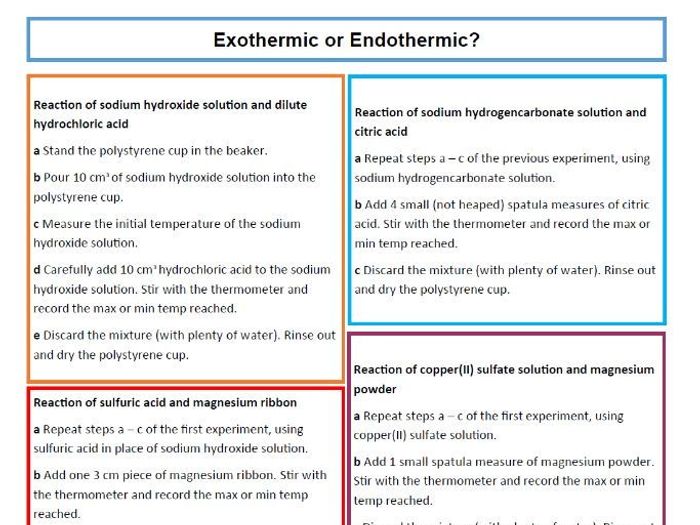
The following table compares the characteristics of endothermic and exothermic reactions:
| Characteristic | Endothermic Reactions | Exothermic Reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Energy change | Positive (energy absorbed) | Negative (energy released) |
| Temperature change | Temperature decreases | Temperature increases |
| Examples | Melting of ice, boiling of water | Burning of wood, rusting of iron |
Applications of Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions: Endothermic Vs Exothermic Worksheet Answers
Endothermic reactions are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Cooling systems (e.g., air conditioners, refrigerators)
- Desalination of seawater
- Production of chemicals (e.g., ammonia, sulfuric acid)
Exothermic reactions are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Heating systems (e.g., furnaces, boilers)
- Production of electricity (e.g., combustion engines, fuel cells)
- Explosives (e.g., dynamite, TNT)
Key Questions Answered
What is the key difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions?
Endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings, while exothermic reactions release energy into their surroundings.
Provide an example of an endothermic reaction.
Dissolving ammonium chloride in water is an endothermic reaction.
How are exothermic reactions utilized in everyday life?
Exothermic reactions are harnessed in various applications, including the combustion of fuels, hand warmers, and glow sticks.
