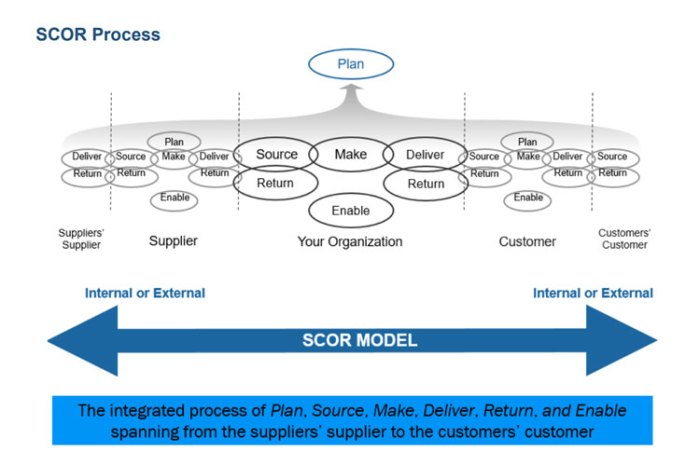
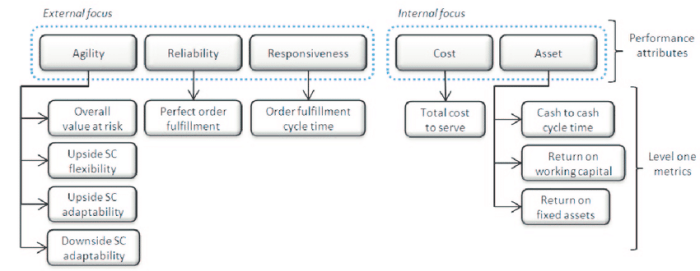
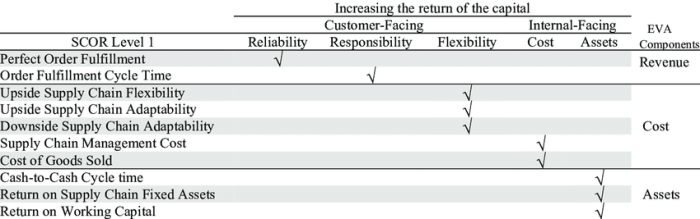
The SCOR model provides suggested metrics that serve as a valuable tool for organizations seeking to measure and enhance their performance. This framework offers a comprehensive approach to identifying and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with specific business objectives.
By leveraging the SCOR model’s suggested metrics, organizations can gain actionable insights into their operations, driving continuous improvement and optimizing outcomes.
The SCOR model categorizes metrics into various types, including performance, quality, timeliness, and cost. These metrics are meticulously calculated using standardized methodologies, ensuring consistency and comparability across different departments and functions. By analyzing the data gathered from these metrics, organizations can pinpoint areas for improvement, benchmark their performance against industry best practices, and implement targeted strategies for enhancing efficiency and effectiveness.
1. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): The Scor Model Provides Suggested Metrics
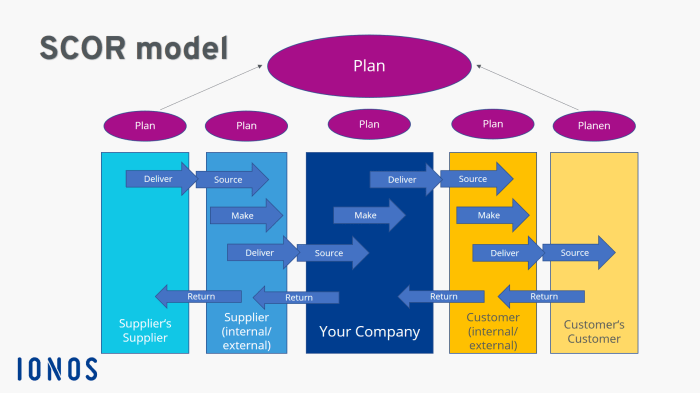
KPIs are essential for measuring the effectiveness of a model. They provide a quantitative way to track progress and identify areas for improvement. The SCOR model provides a comprehensive set of KPIs that can be used to measure the performance of supply chain processes.
Specific KPIs provided by the SCOR model include:
- Cost to serve
- Inventory turnover
- Order fulfillment cycle time
- Customer satisfaction
These KPIs can be used to track performance over time and identify areas for improvement. For example, if a company’s inventory turnover is low, it may indicate that the company is holding too much inventory. This could lead to increased costs and decreased efficiency.
2. Metrics and Measurement, The scor model provides suggested metrics
The SCOR model uses a variety of metrics to measure the performance of supply chain processes. These metrics can be divided into two categories: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative metrics are based on numerical data. Examples of quantitative metrics include:
- Cost
- Time
- Quantity
Qualitative metrics are based on subjective data. Examples of qualitative metrics include:
- Customer satisfaction
- Employee satisfaction
- Supplier performance
The SCOR model provides a table that compares different types of metrics used in the model. This table can be used to help organizations select the right metrics for their specific needs.
3. Data Collection and Analysis
The SCOR model provides a framework for collecting and analyzing data. This framework includes the following steps:
- Identify the data that needs to be collected.
- Determine how the data will be collected.
- Collect the data.
- Analyze the data.
- Use the data to improve performance.
The SCOR model provides a variety of tools and techniques that can be used to collect and analyze data. These tools and techniques include:
- Surveys
- Interviews
- Focus groups
- Data mining
- Statistical analysis
Data analysis can be used to identify areas for improvement. For example, if a company’s customer satisfaction scores are low, data analysis can be used to identify the root cause of the problem.
4. Benchmarking and Best Practices
Benchmarking is the process of comparing an organization’s performance to that of other organizations. Benchmarking can be used to identify best practices and improve performance.
The SCOR model provides a framework for benchmarking supply chain performance. This framework includes the following steps:
- Identify the organizations that will be benchmarked.
- Collect data on the performance of the benchmarked organizations.
- Compare the data to the performance of the organization.
- Identify areas for improvement.
The SCOR model can be used to identify best practices in supply chain management. Best practices are processes or techniques that have been proven to improve performance. By implementing best practices, organizations can improve their supply chain performance.
5. Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is the process of making ongoing improvements to a process. The SCOR model provides a framework for continuous improvement. This framework includes the following steps:
- Identify the process that needs to be improved.
- Analyze the process.
- Identify areas for improvement.
- Make the improvements.
- Monitor the improvements.
Continuous improvement is an ongoing process. By continuously improving their supply chain processes, organizations can improve their overall performance.
User Queries
What is the primary purpose of the SCOR model?
The SCOR model is designed to provide organizations with a standardized framework for measuring and improving their supply chain performance.
How are metrics calculated within the SCOR model?
Metrics in the SCOR model are calculated using specific formulas and methodologies, ensuring consistency and comparability across different organizations.
What are the benefits of using the SCOR model for performance improvement?
The SCOR model helps organizations identify areas for improvement, benchmark their performance against industry best practices, and implement targeted strategies for enhancing efficiency and effectiveness.